...
You want to import existing data in CSV format for use in Konect. You may want to either create a new dataset or append records to an existing dataset.
Existing datasets may be available as CSV files as CSV is a particularly common data exchange format. CSV files can be brought into Konect and mapped as point features.
CSV files can be interpreted by Konect Manager as point feature GIS files if they have two columns that contain the longitude and latitude of point objects in the WGS 84 coordinate system.
STEP-BY-STEP
...
STEP-BY-STEP
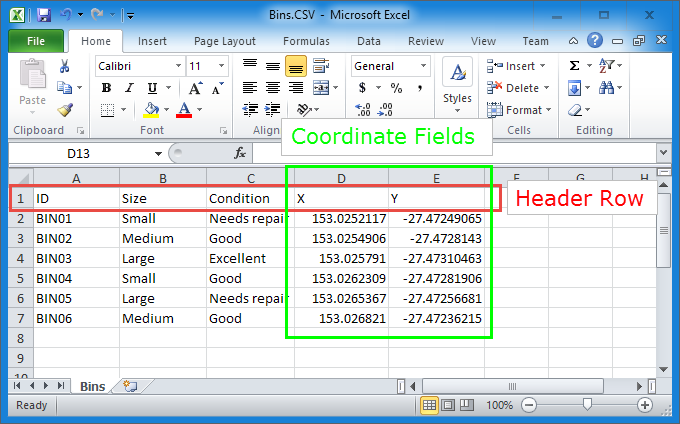
CSV Structure
These instructions assume that you understand what a CSV file is and how the display of a CSV file will vary depending on the application you use to view it. If you require more information on CSV basic follow this link:
For this discussion we will be using MS Excel to view and discuss the structure of CSV files.
Konect will recognise a CSV file as a capable of being imported and mapped if three requirements are met:
1. It must have a header row
2. It must have coordinate fields
3. The coordinates must be recorded as Latitude and Longitude (WGS 84 projection) but the field names can be whatever you like
If the two coordinate columns have the names ‘X’ and ‘Y’, then
...
Konect will recognise these as coordinate fields and commence the import process. However, if the coordinate columns are not called ‘X’ and ‘Y’, then Konect
...
prompts the user to select which columns contain
...
As an example, import the file ‘Bins.CSV’ (available for download at Bins.zip) which stores the longitude and latitude in the columns ‘Long’ and ‘Lat’.
...
the longitude
...
and
...
latitude
...
.
...
Go to the ‘Data’ tab and select the ‘Bins’ dataset to view the 6 bins that are along the streets George and Mary in the city of Brisbane, Australia.
The grid at the bottom of the ‘Data’ tab gives the aspatial bin information.
Note: the order of the records is not the same as in the file ‘Bins.CSV’.
Creating A New Dataset
Use the following steps to create a new dataset by importing a CSV file:
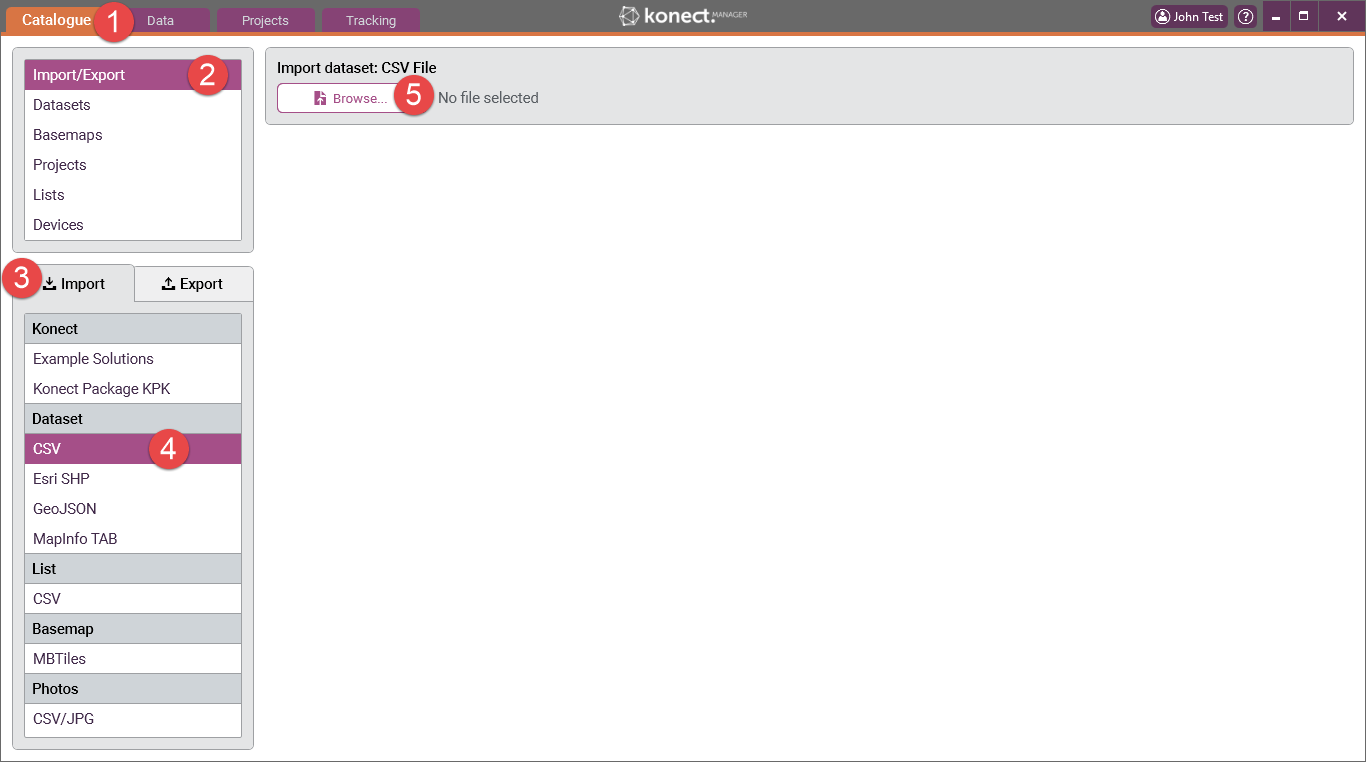
1 Go to the ‘Catalogue’ tab in Konect Manager.
2 Select the ‘Import/Export’
3 Select the ‘Import’ tab.
4 Select ‘CSV' in the ‘Dataset’ list. NOTE: The CSV file must not be open in any other application for the import to proceed
5 Press the ‘Browse’ button. Select and 'Open' the required file. In this example ‘Bins.csv' has been used.
Where the CSV File HAS "X" and "Y" Coordinate Fields
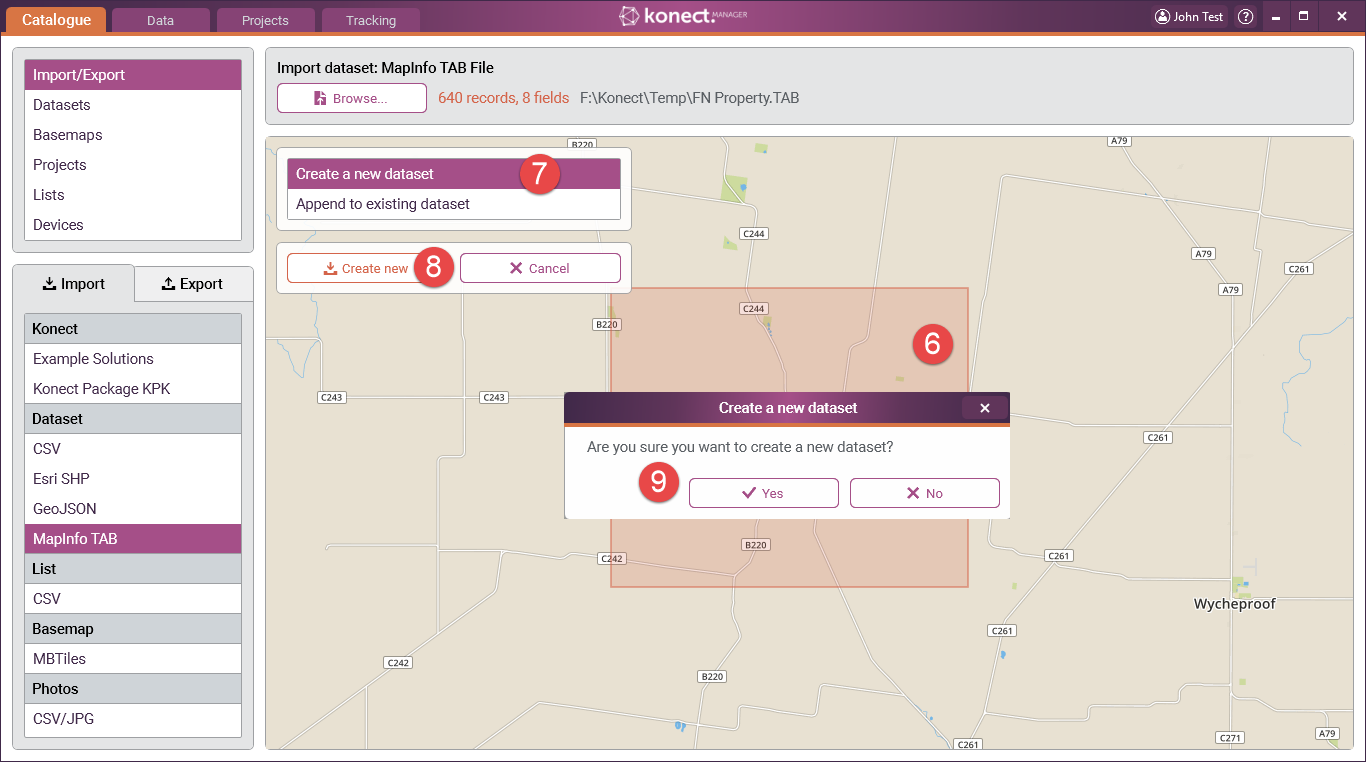
6 If the CSV file has fields with the names "X" and "Y" and these fields contain valid longitude and latitude values respectively, Konect will automatically recognise these and, Konect Manager reads the contents of the selected file and displays the number of records and the number of data fields in the file. It also draws a rectangle, called the bounding rectangle, that geographically encompasses all the map features in the file. The user can use this information to check that the correct data is being imported.
Konect performs a comparison between the dataset being imported and all existing datasets in Konect. If the data structure matches in any way you will be presented with the option of either 'Creating a new dataset' or 'Appending to an existing dataset'.
If there is no match then you are only given the option of 'Creating a new dataset'
7 If required, select 'Create a new dataset' from the options box
8 Select 'Create new'
9 Click 'Yes' when prompted to create the dataset
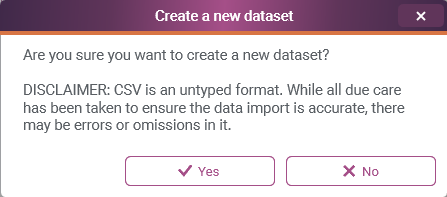
10 A confirmation dialog will present. The warning information relates to potential difficulty that Konect may have in interpreting some data formats, in particular date and boolean (logical) data. Click 'Yes'.
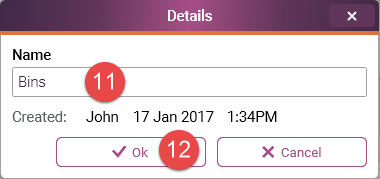
11 Enter the name that you want to give to the dataset. In this example "Bins".
12 Press the 'Ok' button.
13 The CSV file is imported and Konect Manager automatically goes to the ‘Datasets’ item in the ‘Catalogue’ from where various data settings can be set, added or modified.
Where the CSV File DOES NOT HAVE "X" and "Y" Coordinate Fields
6 If the CSV file does not have fields called "X" and "Y", Konect will prompt you to select the fields to be used. Any suitable numeric field will be available for selection from the pick lists. In this example there are only two possible choices and these just happened to be named "Latitude" and "Longitude" to make it easier to select the correct field.
Select the fields for Longitude and Latitude
Click 'Ok'
Konect Manager reads the contents of the selected file and displays the number of records and the number of data fields in the file. It also draws a rectangle, called the bounding rectangle, that geographically encompasses all the map features in the file. The user can use this information to check that the correct data is being imported.
...
9 Click 'Yes' when prompted to create the dataset
...
10 A confirmation dialog will present. The warning information relates to potential difficulty that Konect may have in interpreting some data formats, in particular date and boolean (logical) data. Click 'Yes'.
11 Enter the name that you want to give to the dataset. In this example "PropertyBins".
11 12 Press the 'Ok' button.
12 The TAB 13 The CSV file is imported and Konect Manager automatically goes to the ‘Datasets’ item in the ‘Catalogue’ from where various data settings can be set, added or modified.
...
Append To An Existing Dataset
Records can be appended (added) to an existing Use the following steps to append a dataset by importing a TAB CSV file.:
1 Go to the ‘Catalogue’ tab in Konect Manager.
2 Select the ‘ImportSelect ‘Import/Export’
3 Select the ‘Import’ tab.
4 Select ‘MapInfo TAB’ ‘CSV' in the ‘Dataset’ list. NOTE: The CSV file must not be open in any other application for the import to proceed
5 Press the ‘Browse’ button. Select and 'Open' the required file. In this example we have used ‘FN Property.TAB’
6 ‘Bins.csv' has been used.
Where the CSV File HAS "X" and "Y" Coordinate Fields
6 If the CSV file has fields with the names "X" and "Y" and these fields contain valid longitude and latitude values respectively, Konect Manager reads the contents of the selected file and displays the number of records and the number of data fields in the file. It also draws a rectangle, called the bounding rectangle, that geographically encompasses all the map features in the file. The user You can use this information to check that the correct data is being imported.7 Select
Konect performs a comparison between the dataset being imported and all existing datasets in Konect. If the data structure matches in any way (at least one field) you will be presented with the option of either 'Creating a new dataset' or 'Appending to an existing dataset'.
If there is no match then you are only given the option of 'Creating a new dataset'
7 Select 'Append to existing dataset' from the options box. This option
8 The dataset selection box will only present if there is a full or partial match between the file being imported and any Konect datasets.
8 This will cause the "Choose dataset to append' box to open
9 Open the 'Please select' list and select the dataset you want to append to.
The list shows all the existing Konect datasets that have at least one matching field with the GIS file. It also shows the number of fields that match. For a field to match it must have:
- The same name as a field in the existing Konect dataset.
- A type that can be converted to the type of field in the existing Konect dataset. For example, if there is a Text field called ID in the existing dataset and a Number field called ID in the import file, then these two fields are a match because a number can always be converted to its textual representation. However, if the field ID in the existing dataset is a Number field and the field ID in the import file is a Text field then these two fields are not a match because text cannot always be converted to a number.
If the mouse is hovered over an item in the dropdown list, the matching fields are displayed.
After choosing a dataset to append to, Konect Manager shows which fields are not matched, if there are any.
10 Select 'Append dataset'
11 Click 'Yes' when prompted to create the dataset
12 The records are . Choose the dataset you want to append to from the list
9 Select 'Append dataset'
10 A confirmation dialog will present. The warning information relates to potential difficulty that Konect may have in interpreting some data formats, in particular date and boolean (logical) data. Click 'Yes'.
11 The CSV file is imported and Konect Manager automatically goes to the ‘Datasets’ item in the ‘Catalogue’ from where various data settings can be set, added or modified.
Where the CSV File DOES NOT HAVE "X" and "Y" Coordinate Fields
6 If the CSV file does not have fields called "X" and "Y", Konect will prompt you to select the fields to be used. Any suitable numeric field will be available for selection from the pick lists. In this example there are only two possible choices and these just happened to be named "Latitude" and "Longitude" to make it easier to select the correct field.
7. Select the fields for Longitude and Latitude
8. Click 'Ok'
Konect Manager reads the contents of the selected file and displays the number of records and the number of data fields in the file. It also draws a rectangle, called the bounding rectangle, that geographically encompasses all the map features in the file. The user can use this information to check that the correct data is being imported.
Konect performs a comparison between the dataset being imported and all existing datasets in Konect. If the data structure matches in any way you will be presented with the option of either 'Creating a new dataset' or 'Appending to an existing dataset'.
If there is no match then you are only given the option of 'Creating a new dataset'
9 Select 'Append to existing dataset' from the options box
10 The dataset selection box will present. Choose the dataset you want to append to from the list
11 Select 'Append dataset'
12 A confirmation dialog will present. The warning information relates to potential difficulty that Konect may have in interpreting some data formats, in particular date and boolean (logical) data. Click 'Yes'.
13 The CSV file is appended and Konect Manager automatically goes to the ‘Datasets’ item in the ‘Catalogue’..